Introduction
Last week we discussed advances in Gaussian Splatting and the impact on text-to-video content creation within the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, these technologies are making significant strides and changing the way we think about content creation. Today we will discuss another technological advancement; Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and its impact on text-to-video AI. When these technologies converge, they unlock new possibilities for content creators, offering unprecedented levels of realism, customization, and efficiency. In this blog post, we will delve deep into these technologies, focusing particularly on their integration in OpenAI’s latest product, Sora, and explore their implications for the future of digital content creation.
Understanding Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF)
NeRF represents a groundbreaking approach to rendering 3D scenes from 2D images with astonishing detail and photorealism. This technology uses deep learning to interpolate light rays as they travel through space, capturing the color and intensity of light at every point in a scene to create a cohesive and highly detailed 3D representation. For content creators, NeRF offers a way to generate lifelike environments and objects from a relatively sparse set of images, reducing the need for extensive 3D modeling and manual texturing.
Expanded Understanding of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF)
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) is a novel framework in the field of computer vision and graphics, enabling the synthesis of highly realistic images from any viewpoint using a sparse set of 2D input images. At its core, NeRF utilizes a fully connected deep neural network to model the volumetric scene functionally, capturing the intricate play of light and color in a 3D space. This section aims to demystify NeRF for technologists, illustrating its fundamental concepts and practical applications to anchor understanding.
Fundamentals of NeRF
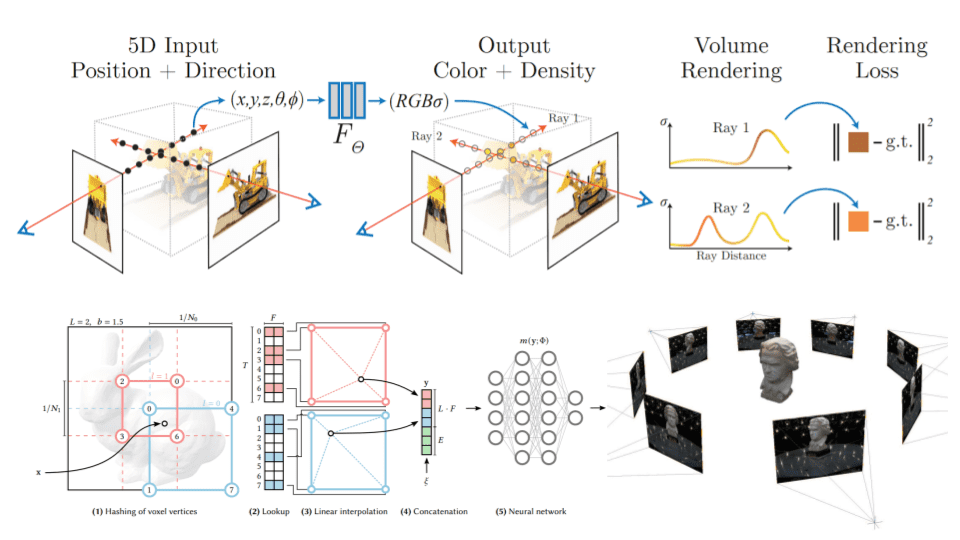
NeRF represents a scene using a continuous 5D function, where each point in space (defined by its x, y, z coordinates) and each viewing direction (defined by angles θ and φ) is mapped to a color (RGB) and a volume density. This mapping is achieved through a neural network that takes these 5D coordinates as input and predicts the color and density at that point. Here’s how it breaks down:
- Volume Density: This measure indicates the opaqueness of a point in space. High density suggests a solid object, while low density implies empty space or transparency.
- Color Output: The predicted color at a point, given a specific viewing direction, accounts for how light interacts with objects in the environment.
When rendering an image, NeRF integrates these predictions along camera rays, a process that simulates how light travels and scatters in a real 3D environment, culminating in photorealistic image synthesis.
Training and Rendering
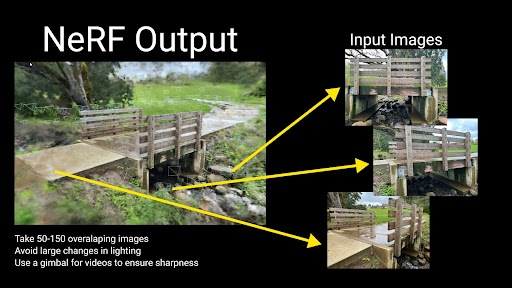
To train a NeRF model, you need a set of images of a scene from various angles, each with its corresponding camera position and orientation. The training process involves adjusting the neural network parameters until the rendered views match the training images as closely as possible. This iterative optimization enables NeRF to interpolate and reconstruct the scene with high fidelity.
During rendering, NeRF computes the color and density for numerous points along each ray emanating from the camera into the scene, aggregating this information to form the final image. This ray-marching process, although computationally intensive, results in images with impressive detail and realism.
Practical Examples and Applications
- Virtual Tourism: Imagine exploring a detailed 3D model of the Colosseum in Rome, created from a set of tourist photos. NeRF can generate any viewpoint, allowing users to experience the site from angles never captured in the original photos.
- Film and Visual Effects: In filmmaking, NeRF can help generate realistic backgrounds or virtual sets from a limited set of reference photos, significantly reducing the need for physical sets or extensive location shooting.
- Cultural Heritage Preservation: By capturing detailed 3D models of historical sites or artifacts from photographs, NeRF aids in preserving and studying these treasures, making them accessible for virtual exploration.
- Product Visualization: Companies can use NeRF to create realistic 3D models of their products from a series of photographs, enabling interactive customer experiences online, such as viewing the product from any angle or in different lighting conditions.
Key Concepts in Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF)
To understand Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) thoroughly, it is essential to grasp its foundational concepts and appreciate how these principles translate into the generation of photorealistic 3D scenes. Below, we delve deeper into the key concepts of NeRF, providing examples to elucidate their practical significance.
Scene Representation
NeRF models a scene using a continuous, high-dimensional function that encodes the volumetric density and color information at every point in space, relative to the viewer’s perspective.
- Example: Consider a NeRF model creating a 3D representation of a forest. For each point in space, whether on the surface of a tree trunk, within its canopy, or in the open air, the model assigns both a density (indicating whether the point contributes to the scene’s geometry) and a color (reflecting the appearance under particular lighting conditions). This detailed encoding allows for the realistic rendering of the forest from any viewpoint, capturing the nuances of light filtering through leaves or the texture of the bark on the trees.
Photorealism
NeRF’s ability to synthesize highly realistic images from any perspective is one of its most compelling attributes, driven by its precise modeling of light interactions within a scene.
- Example: If a NeRF model is applied to replicate a glass sculpture, it would capture how light bends through the glass and the subtle color shifts resulting from its interaction with the material. The end result is a set of images so detailed and accurate that viewers might struggle to differentiate them from actual photographs of the sculpture.
Efficiency
Despite the high computational load required during the training phase, once a NeRF model is trained, it can render new views of a scene relatively quickly and with fewer resources compared to traditional 3D rendering techniques.
- Example: After a NeRF model has been trained on a dataset of a car, it can generate new views of this car from angles not included in the original dataset, without the need to re-render the model entirely from scratch. This capability is particularly valuable for applications like virtual showrooms, where potential buyers can explore a vehicle from any angle or lighting condition, all generated with minimal delay.
Continuous View Synthesis
NeRF excels at creating smooth transitions between different viewpoints in a scene, providing a seamless viewing experience that traditional 3D models struggle to match.
- Example: In a virtual house tour powered by NeRF, as the viewer moves from room to room, the transitions are smooth and realistic, with no abrupt changes in texture or lighting. This continuous view synthesis not only enhances the realism but also makes the virtual tour more engaging and immersive.
Handling of Complex Lighting and Materials
NeRF’s nuanced understanding of light and material interaction enables it to handle complex scenarios like transparency, reflections, and shadows with a high degree of realism.
- Example: When rendering a scene with a pond, NeRF accurately models the reflections of surrounding trees and the sky in the water, the transparency of the water with varying depths, and the play of light and shadow on the pond’s bed, providing a remarkably lifelike representation.
The key concepts of NeRF—scene representation, photorealism, efficiency, continuous view synthesis, and advanced handling of lighting and materials—are what empower this technology to create stunningly realistic 3D environments from a set of 2D images. By understanding these concepts, technologists and content creators can better appreciate the potential applications and implications of NeRF, from virtual reality and filmmaking to architecture and beyond. As NeRF continues to evolve, its role in shaping the future of digital content and experiences is likely to expand, offering ever more immersive and engaging ways to interact with virtual worlds.
Advancements in Text-to-Video AI
Parallel to the developments in NeRF, text-to-video AI technologies are transforming the content landscape by enabling creators to generate video content directly from textual descriptions. This capability leverages advanced natural language processing and deep learning techniques to understand and visualize complex narratives, scenes, and actions described in text, translating them into engaging video content.
Integration with NeRF:
- Dynamic Content Generation: Combining NeRF with text-to-video AI allows creators to generate realistic 3D environments that can be seamlessly integrated into video narratives, all driven by textual descriptions.
- Customization and Flexibility: Content creators can use natural language to specify details about environments, characters, and actions, which NeRF and text-to-video AI can then bring to life with high fidelity.
OpenAI’s Sora: A Case Study in NeRF and Text-to-Video AI Convergence
OpenAI’s Sora exemplifies the integration of NeRF and text-to-video AI, illustrating the potential of these technologies to revolutionize content creation. Sora leverages NeRF to create detailed, realistic 3D environments from textual inputs, which are then animated and rendered into dynamic video content using text-to-video AI algorithms.
Implications for Content Creators:
- Enhanced Realism: Sora enables the production of videos with lifelike environments and characters, raising the bar for visual quality and immersion.
- Efficiency: By automating the creation of complex scenes and animations, Sora reduces the time and resources required to produce high-quality video content.
- Accessibility: With Sora, content creators do not need deep technical expertise in 3D modeling or animation to create compelling videos, democratizing access to advanced content creation tools.
Conclusion
The integration of NeRF and text-to-video AI, as demonstrated by OpenAI’s Sora, marks a significant milestone in the evolution of content creation technology. It offers content creators unparalleled capabilities to produce realistic, engaging, and personalized video content efficiently and at scale.
As we look to the future, the continued advancement of these technologies will further expand the possibilities for creative expression and storytelling, enabling creators to bring even the most ambitious visions to life. For junior practitioners and seasoned professionals alike, understanding the potential and applications of NeRF and text-to-video AI is essential for staying at the forefront of the digital content creation revolution.
In conclusion, the convergence of NeRF and text-to-video AI is not just a technical achievement; it represents a new era in storytelling, where the barriers between imagination and reality are increasingly blurred. For content creators and consumers alike, this is a journey just beginning, promising a future rich with possibilities that are as limitless as our creativity.




