Introduction
Yesterday, we introduced the topics of quantum computing and materials and today we will welcome quantum physics into the conversation and dive another level deeper. By discussing all three within the mechanical engineering space, we hope to provide a view into how all three are being leveraged by this discipline and what that future may look like.
In an era where technological advancements are not just innovations but revolutions, the fields of quantum computing, quantum physics, and quantum materials are emerging as pivotal game-changers. This blog post delves into these complex yet fascinating domains, focusing particularly on their intersection with mechanical engineering and their multifaceted applications in both public and private sectors.
Foundations of Quantum Computing and Quantum Physics

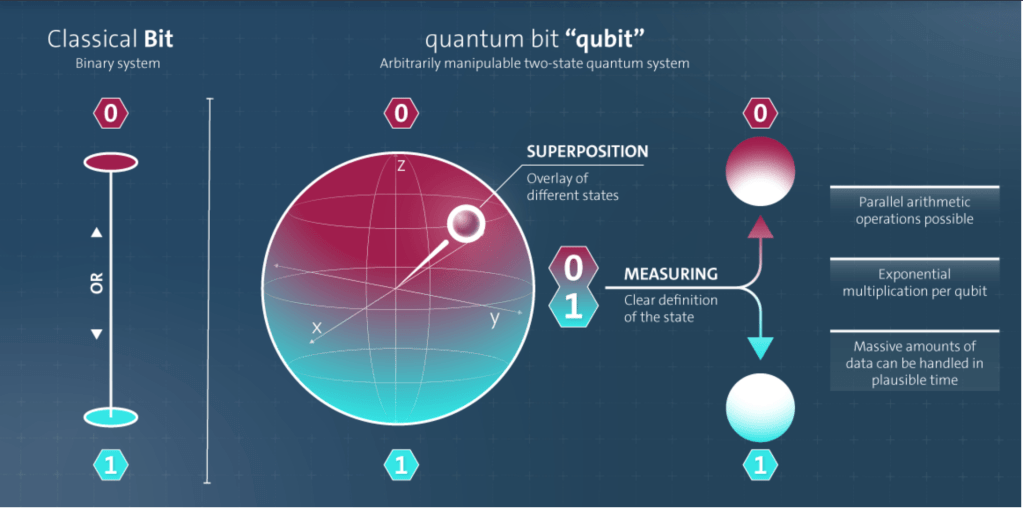
Quantum computing and quantum physics are intrinsically linked, with the former being a practical application of the principles of the latter. Quantum physics, the study of the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest scales, lays the groundwork for quantum computing. Unlike classical computing, which relies on bits (0s and 1s), quantum computing uses quantum bits or qubits. These qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously, thanks to the principles of superposition and entanglement, which are cornerstones of quantum mechanics.
Quantum Materials: The New Frontier
Quantum materials are substances that exhibit exotic properties governed by the principles of quantum mechanics. These materials, such as topological insulators, superconductors, and graphene, show immense promise in revolutionizing various fields, including mechanical engineering.
Quantum Materials in Mechanical Engineering: Use Cases
Public Sector Applications
- Energy Storage and Conversion: Quantum materials like graphene are being explored for their potential in improving the efficiency of solar cells and batteries. Public institutions are investing in research to leverage these materials for sustainable and efficient energy solutions.
- Transportation: Superconducting materials, a subset of quantum materials, could revolutionize public transportation. Their application in magnetic levitation (maglev) trains exemplifies how they can reduce friction and energy consumption, leading to faster and more efficient transportation.
Private Sector Applications
- Electronics Industry: The miniaturization and enhanced performance of electronic components, crucial in today’s digital world, are achievable through quantum materials. Private companies are exploring materials like topological insulators for developing next-generation semiconductors.
- Aerospace and Defense: Quantum materials are critical in developing advanced materials for aerospace, where weight, strength, and thermal properties are paramount. Private aerospace firms are researching quantum materials for applications in spacecraft and aviation technology.
Advantages and Challenges
Advantages
- Enhanced Performance: Quantum materials offer superior properties, like high conductivity and unique magnetic characteristics, which can lead to breakthroughs in various technologies.
- Innovation in Various Fields: From energy to healthcare, the application of quantum materials paves the way for innovations across multiple sectors.
Challenges
- High Cost and Complexity: The synthesis and manipulation of quantum materials are often expensive and complex, making them currently less accessible for widespread use.
- Lack of Understanding: The nascent stage of quantum material research implies a limited understanding, which poses challenges in their practical application.
Quantum Materials: Real-World Business Applications
Quantum materials are not just theoretical constructs but have practical implications in addressing day-to-day business challenges. Companies like IBM and Google are investing in quantum computing, eyeing its potential to solve complex computational problems. In the energy sector, quantum materials are seen as the key to developing more efficient renewable energy systems. Meanwhile, in healthcare, their application in drug discovery and medical imaging represents a frontier of innovation.
Organizations Leading the Charge
Several organizations are proactively addressing the challenges and opportunities presented by quantum materials. Institutes like the Stewart Blusson Quantum Materials Institute (QMI) and companies such as QuantumScape and Rigetti Computing are at the forefront of this endeavor. Their focus ranges from fundamental research to the development of practical applications.
Conclusion
Quantum computing, physics, and materials represent a convergence of science and engineering that holds the promise of transformative changes across industries. As we continue to explore these realms, the potential for innovation in mechanical engineering and beyond is boundless. Stay tuned to this blog for more insights into the world of quantum materials, where the future of technology is being written today.
Engage with our ongoing exploration of quantum materials by following our posts. Discover the impact of these advanced materials in reshaping industries and driving technological progress. Don’t miss out on the journey to the forefront of innovation – follow us for the latest updates and in-depth analyses.