Introduction
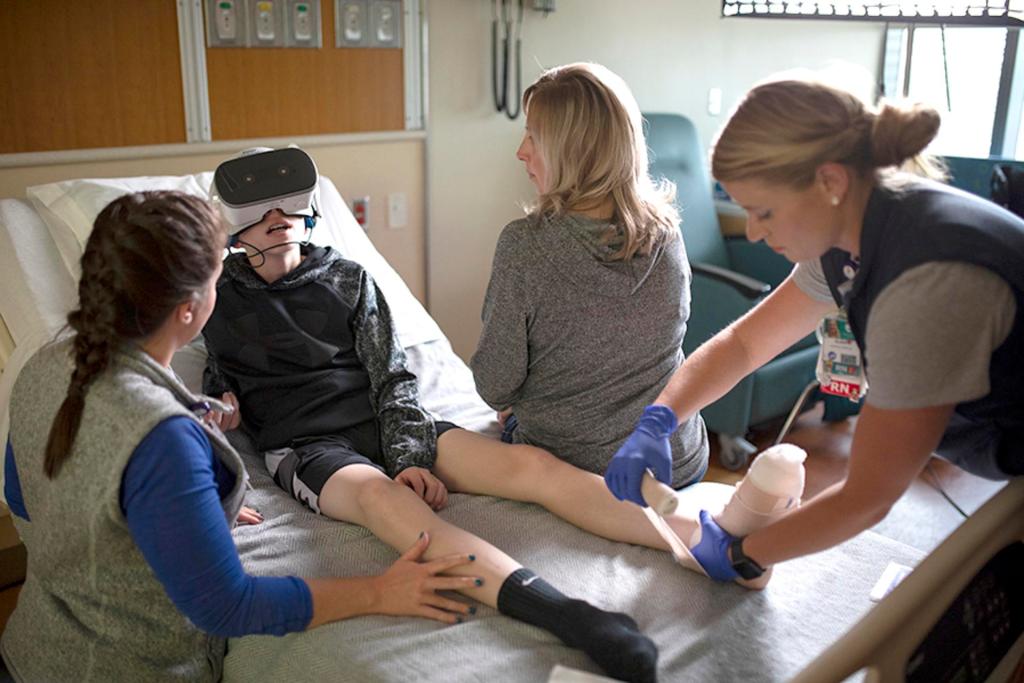
Virtual Reality (VR) technology, once a staple of science fiction, has rapidly become a tangible and influential tool in various sectors, including healthcare and education. Among its most promising applications is its use in assisting individuals with Intellectual Developmental Disorders (IDD). This technology is not only revolutionizing therapeutic approaches but also offering unique opportunities for addressing the developmental challenges faced by adolescents with IDD. In this blog post, we will delve into the benefits and disadvantages of VR in this context, exploring real-world examples and future potential.
Understanding Intellectual Developmental Disorders
Intellectual Developmental Disorders encompass a range of cognitive impairments that affect learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and adaptive behavior. Adolescents with IDD face unique challenges in their development, often requiring tailored support to navigate their daily lives and integrate into society effectively.
The Advantages of VR in IDD Therapies
Immersive Learning Environments
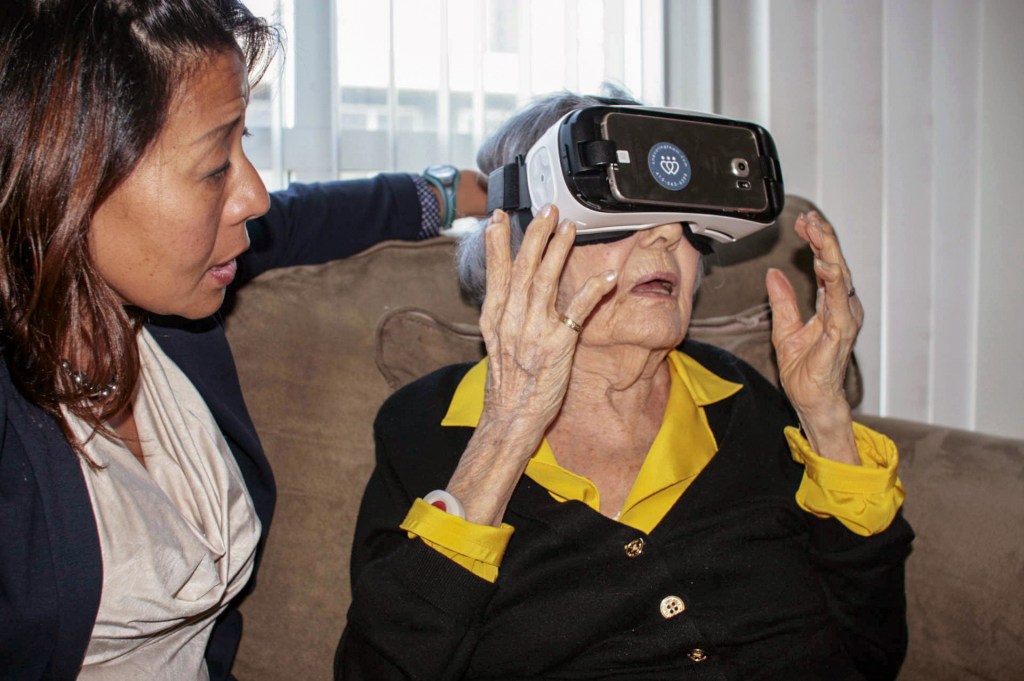
VR creates immersive, controlled environments that are particularly beneficial for adolescents with IDD. These environments can be customized to the individual’s learning pace and cognitive level, offering a safe space to learn and practice life skills. For instance, a VR program can simulate a grocery store, allowing users to practice shopping, handling money, and social interactions in a realistic yet controlled setting.
Enhanced Engagement and Motivation
The engaging nature of VR can significantly increase motivation in learning and therapy sessions. Adolescents are more likely to participate actively in VR-based activities, which are often perceived as more of a game than traditional therapy or learning methods.
Improved Cognitive and Motor Skills
VR applications have shown promise in enhancing cognitive functions like attention, memory, and problem-solving. Additionally, certain VR programs are designed to improve fine motor skills and coordination, essential for adolescents with IDD who may struggle with these aspects.
Emotional and Social Skill Development
VR scenarios can be tailored to teach emotional recognition and social interaction skills. By simulating various social situations, adolescents with IDD can learn and practice appropriate emotional responses and social behaviors in a low-risk environment.
The Disadvantages and Challenges
Accessibility and Cost
One of the main barriers to widespread VR adoption in IDD therapies is the cost and accessibility of the technology. High-quality VR systems can be expensive, and not all therapy centers or schools may have the resources to implement them.
Potential Overstimulation
VR experiences can sometimes be overwhelming, especially for individuals with sensory processing difficulties common in IDD. Overstimulation can lead to discomfort or anxiety, potentially negating the benefits of the therapy.
Limited Research and Standardization
While VR in IDD therapy shows great promise, there is still a lack of extensive research and standardized protocols. This gap can lead to inconsistent outcomes and difficulties in integrating VR therapies into established treatment plans.
Real-World Examples and Future Potential
Case Studies in Education and Therapy
Several schools and therapy centers have started integrating VR into their programs with positive results. For example, a special education school in the United States has used VR to teach road safety and public transportation navigation. In another case, a therapy center in Europe employs VR to help adolescents with IDD improve social skills through simulated interactions.
Future Directions
The future of VR in IDD therapy is bright, with ongoing research and development aimed at creating more accessible, tailored, and effective VR solutions. Future advancements may include AI-driven VR environments that adapt in real-time to the user’s responses, further personalizing the learning experience.
Conclusion
Virtual Reality presents a groundbreaking avenue for enhancing the lives of adolescents with Intellectual Developmental Disorders. Its immersive, engaging, and customizable nature makes it an effective tool for addressing the unique developmental challenges faced by this group. While there are challenges to overcome, particularly in terms of accessibility and standardization, the potential benefits are immense. As technology continues to advance, we can anticipate even more innovative and impactful applications of VR in this field.
Stay tuned for more insights and updates on the ever-evolving world of Virtual Reality. Follow us for future posts that delve deeper into the intersection of technology and healthcare, exploring how emerging tech is reshaping therapeutic practices and enhancing lives.
Interested in more content like this? Follow our blog for regular updates on the latest trends in technology, healthcare, and education. Discover how cutting-edge technologies like VR are transforming industries and improving lives.
Keywords: Virtual Reality, Intellectual Developmental Disorders, VR Therapy, Adolescent Development, Technology in Healthcare, Innovative Learning Tools, Special Education.