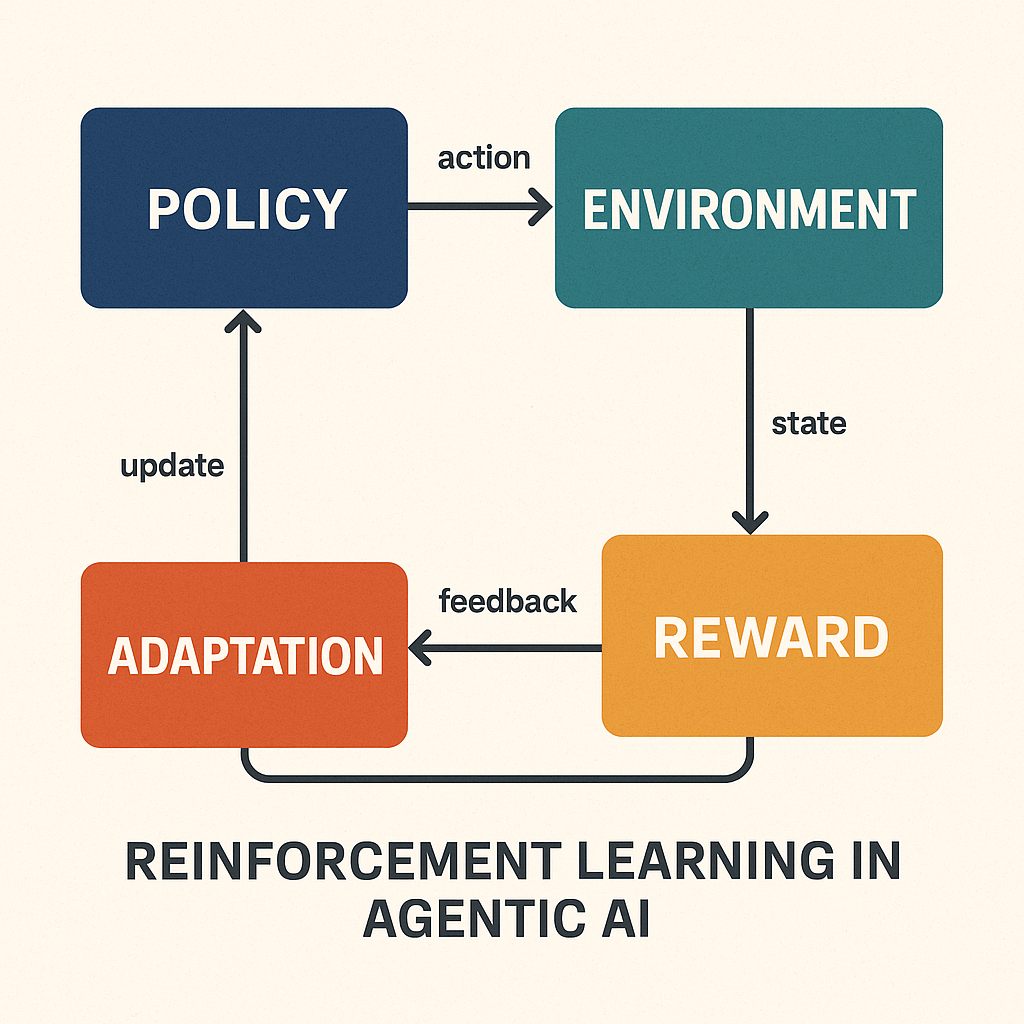
Introduction
The collaboration between OpenAI and OpenClaw is significant because it represents a convergence of two critical layers in the evolving AI stack: advanced cognitive intelligence and autonomous execution. Historically, one domain has focused on building systems that can reason, learn, and generalize, while the other has focused on turning that intelligence into persistent, goal-directed action across real digital environments. Bringing these capabilities closer together accelerates the transition from AI as a responsive tool to AI as an operational system capable of planning, executing, and adapting over time. This has implications far beyond technical progress, influencing platform control, automation scale, enterprise transformation, and the broader trajectory toward more autonomous and generalized intelligence systems.
1. Intelligence vs Execution
Detailed Description
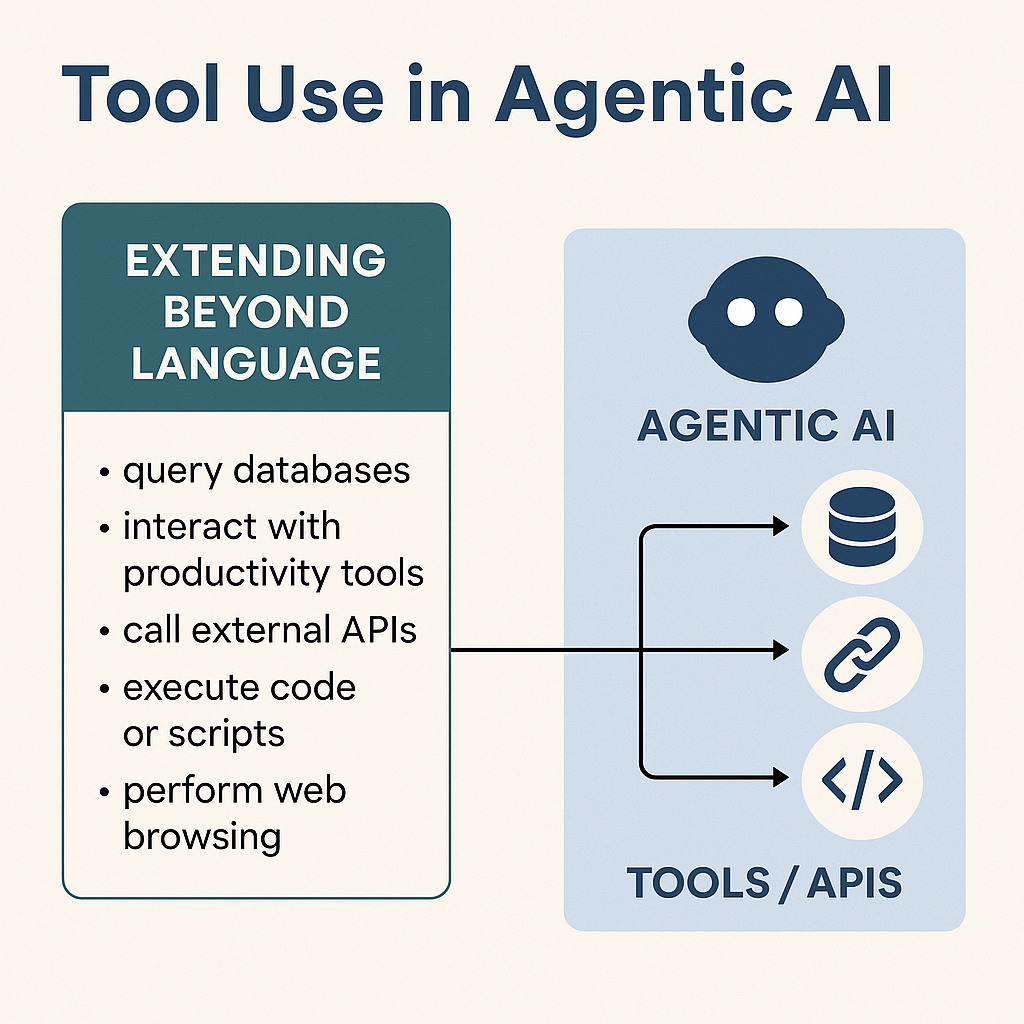
OpenAI has historically focused on creating systems that can reason, generate, understand, and learn across domains. This includes language, multimodal perception, reasoning chains, and alignment. OpenClaw focused on turning intelligence into real-world autonomous action. Execution involves planning, tool use, persistence, and interacting with software environments over time.
In modern AI architecture, intelligence without execution is insight without impact. Execution without intelligence is automation without adaptability. The convergence attempts to unify both.
Examples
Example 1:
An OpenAI model generates a strategic business plan. An OpenClaw agent executes it by scheduling meetings, compiling market data, running simulations, and adjusting timelines autonomously.
Example 2:
An enterprise AI assistant understands a complex customer service scenario. An agent system executes resolution workflows across CRM, billing, and operations platforms without human intervention.
Contribution to the Broader Discussion
This section explains why convergence matters structurally. True intelligent systems require the ability to act, not just think. This directly links to the broader conversation around autonomous systems and long-horizon intelligence, foundational components on the path toward AGI-like capabilities.
2. Model vs Agent Architecture
Detailed Description
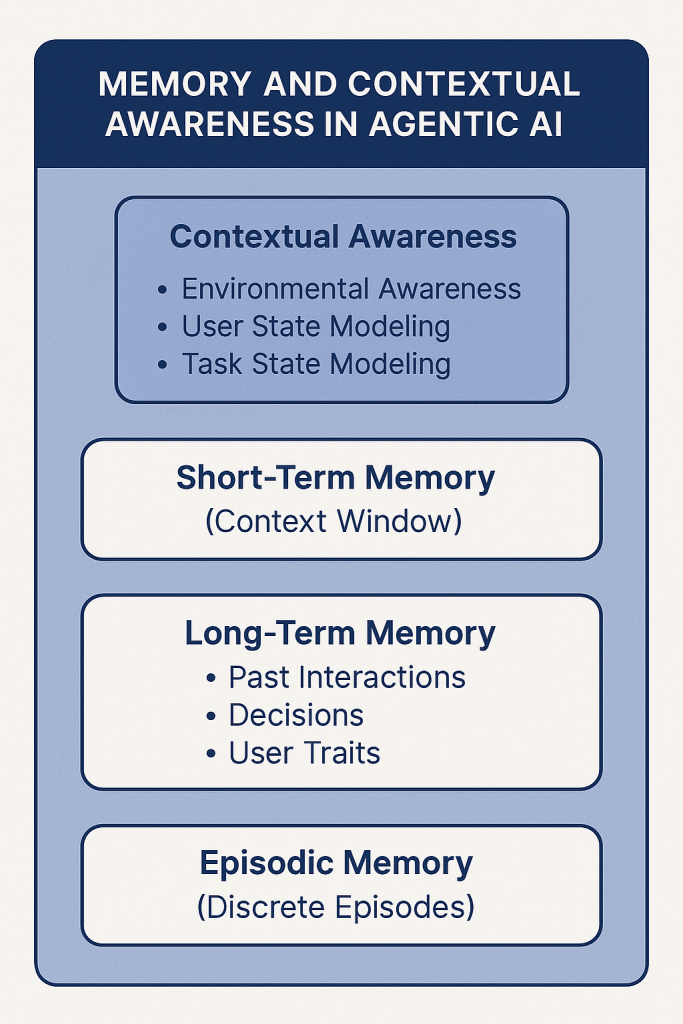
Foundation models are probabilistic reasoning engines trained on massive datasets. Agent architectures layer on top of models and provide memory, planning, orchestration, and execution loops. Models generate intelligence. Agents operationalize intelligence over time.
Agent architecture introduces persistence, goal tracking, multi-step reasoning, and feedback loops, making systems behave more like ongoing processes rather than single interactions.
Examples
Example 1:
A model answers a question about supply chain risk. An agent monitors supply chain data continuously, predicts disruptions, and autonomously reroutes logistics.
Example 2:
A model writes software code. An agent iteratively builds, tests, deploys, monitors, and improves that software over weeks or months.
Contribution to the Broader Discussion
This highlights the shift from static AI to dynamic AI systems. The rise of agent architecture is central to understanding how AI moves from tool to autonomous digital operator, a key theme in consolidation and platform convergence.
3. Research vs Applied Autonomy
Detailed Description
OpenAI has historically invested in long-term AGI research, safety, and foundational intelligence. OpenClaw focused on immediate real-world deployment of autonomous agents. One prioritizes theoretical progress and safe scaling. The other prioritizes operational capability.
This duality reflects a broader industry divide between long-term intelligence and near-term automation.
Examples
Example 1:
A research organization develops a reasoning model capable of complex decision making. An applied agent system deploys it to autonomously manage enterprise workflows.
Example 2:
Advanced reinforcement learning research improves long-horizon reasoning. Autonomous agents use that capability to continuously optimize business operations.
Contribution to the Broader Discussion
This section explains how merging research and deployment accelerates AI progress. The faster research can be translated into real-world execution, the faster AI systems evolve, increasing both opportunity and risk.
4. Platform vs Framework
Detailed Description
OpenAI operates as a vertically integrated AI platform covering models, infrastructure, and ecosystem. OpenClaw functioned as a flexible agent framework that could operate across different model environments. Platforms centralize capability. Frameworks enable flexibility.
The strategic tension is between ecosystem control and ecosystem openness.
Examples
Example 1:
A centralized AI platform offers enterprise-grade agent automation tightly integrated with its model ecosystem. A framework allows developers to deploy agents across multiple model providers.
Example 2:
A platform controls identity, execution, and data pipelines. A framework allows decentralized innovation and modular agent architectures.
Contribution to the Broader Discussion
This section connects directly to consolidation risk and ecosystem dynamics. It frames how platform convergence can accelerate progress while also centralizing control over the future cognitive infrastructure.
5. Strategic Benefits of Alignment
Detailed Description
Combining advanced intelligence with autonomous execution creates a full cognitive stack capable of reasoning, planning, acting, and adapting. This reduces friction between thinking and doing, which is essential for scaling autonomous systems.
Examples
Example 1:
A persistent AI system manages an enterprise transformation program end to end, analyzing data, coordinating stakeholders, and adapting execution dynamically.
Example 2:
A network of autonomous agents runs digital operations, handling customer service, financial forecasting, and product optimization continuously.
Contribution to the Broader Discussion
This explains why such alignment accelerates AI capability. It strengthens the architecture required for large-scale automation and potentially for broader intelligence systems.
6. Strategic Risks and Detriments
Detailed Description
Consolidation can centralize power, expand autonomy risk, reduce competitive diversity, and increase systemic vulnerability. Autonomous systems interacting across platforms create complex adaptive behavior that becomes harder to predict or control.
Examples
Example 1:
A highly autonomous agent system misinterprets objectives and executes actions that disrupt business operations at scale.
Example 2:
Centralized control over agent ecosystems leads to reduced competition and increased dependence on a single platform.
Contribution to the Broader Discussion
This section introduces balance. It reframes the discussion from purely technological progress to systemic risk, governance, and long-term sustainability of AI ecosystems.
7. Practitioner Implications
Detailed Description
AI professionals must transition from focusing only on models to designing autonomous systems. This includes agent orchestration, security, alignment, and multi-agent coordination. The frontier skill set is shifting toward system architecture and platform strategy.
Examples
Example 1:
An AI architect designs a secure multi-agent workflow for enterprise operations rather than building a single predictive model.
Example 2:
A practitioner implements governance, monitoring, and safety layers for autonomous agent execution.
Contribution to the Broader Discussion
This connects the macro trend to individual relevance. It shows how consolidation and agent convergence reshape the AI profession and required competencies.
8. Public Understanding and Societal Implications
Detailed Description
The public must understand that AI is transitioning from passive tool to autonomous actor. The implications are economic, governance-driven, and systemic. The most immediate impact is automation and decision augmentation at scale rather than full AGI.
Examples
Example 1:
Autonomous digital agents manage personal and professional workflows continuously.
Example 2:
Enterprise operations shift toward AI-driven orchestration, changing workforce structures and productivity models.
Contribution to the Broader Discussion
This grounds the technical discussion in societal reality. It reframes AI progress as infrastructure transformation rather than speculative intelligence alone.
9. Strategic Focus as Consolidation Increases
Detailed Description
As consolidation continues, attention must shift toward governance, safety, interoperability, and ecosystem balance. The key challenge becomes managing powerful autonomous systems responsibly while preserving innovation.
Examples
Example 1:
Developing transparent reasoning systems that allow oversight into autonomous decisions.
Example 2:
Maintaining hybrid ecosystems where open-source and centralized platforms coexist.
Contribution to the Broader Discussion
This section connects the entire narrative. It frames consolidation not as an isolated event but as part of a long-term structural shift toward autonomous cognitive infrastructure.
Closing Strategic Synthesis
The convergence of intelligence and autonomous execution represents a transition from AI as a computational tool to AI as an operational system. This shift strengthens the structural foundation required for higher-order intelligence while simultaneously introducing new systemic risks.
The broader discussion is not simply about one partnership or consolidation event. It is about the emergence of persistent autonomous systems embedded across economic, technological, and societal infrastructure. Understanding this transition is essential for practitioners, policymakers, and the public as AI moves toward deeper integration into real-world systems.
Please follow us on (Spotify) as we discuss this and many other similar topics.