
Introduction
While we are exploring the world of Quantum Computing, Materials and Physics this week, we thought that a quick post discussing the foundational aspect of this domain, specifically in the space of quantum computing may be helpful. The buzz seems to be around the word “qubit” – what is it, what does it do, why should I care and if asked, how can I clearly describe this item within an already confusing topic. As we have discussed earlier, quantum computing stands out among the other domains, as it offers unparalleled computational capabilities. At the heart of this revolution lies the qubit. This blog post aims to demystify the qubit, tracing its history, explaining its working principles, and comparing it with classical computing bits.
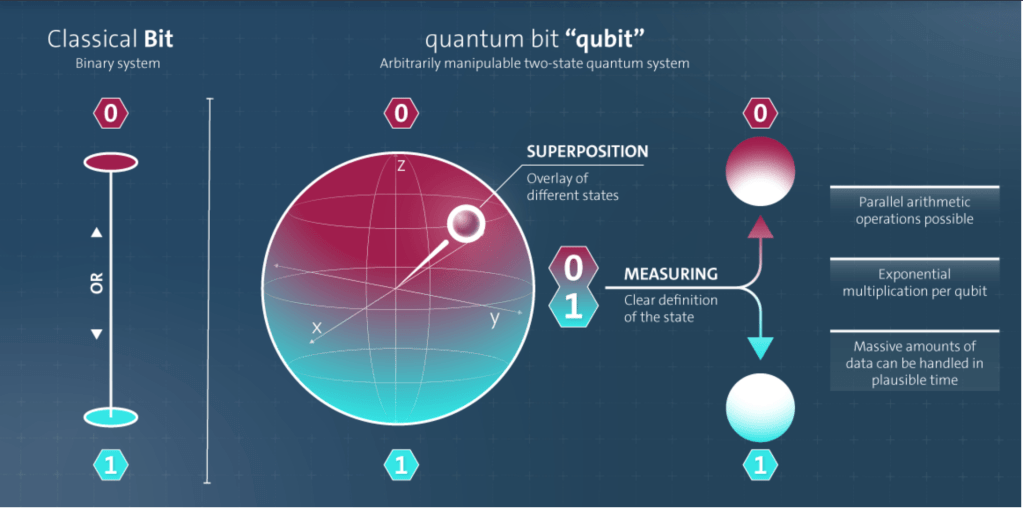
What is a Qubit?
A qubit, or quantum bit, is the basic unit of quantum information. It represents a quantum state that can exist simultaneously in multiple states, unlike a classical bit which is binary. This attribute is due to two fundamental principles of quantum mechanics: superposition and entanglement.
Superposition
Superposition allows a qubit to be in a combination of the 0 and 1 states at the same time, offering a spectrum of possibilities. This contrasts with a classical bit, which is strictly either 0 or 1.
Let’s consider a real-life example of superposition in quantum computing through the context of quantum search algorithms, specifically Grover’s Algorithm, which is designed to find a specific item in an unsorted database.
Example: Finding a Book in a Quantum Library
Imagine a library with a vast collection of books, and you need to find one particular book. In a classical scenario, you would check each book one by one, which is time-consuming. However, in a quantum scenario using Grover’s Algorithm, the process is much more efficient due to superposition.
- Initialization: First, all the books (or data entries) in the library are represented by qubits. Initially, these qubits are put into a state of superposition, where each qubit simultaneously represents all possible books.
- Superposition in Action: Because of superposition, a quantum computer can process all these books simultaneously. It doesn’t look at each book one by one; instead, it examines them all at the same time. This is akin to having a parallel reality where in each one, you’re checking a different book, all happening at once.
- Amplification of the Correct Answer: Through a series of quantum operations, Grover’s Algorithm amplifies the probability of the correct book while diminishing the probabilities of the others. Essentially, the superposition state evolves in such a way that the likelihood of finding the right book increases significantly.
- Observation and Collapse: Once the algorithm completes its processing, the superposition collapses upon observation, leading to the specific book you were searching for. The remarkable aspect is that this happens in a fraction of the time it would take using classical methods.
Implications
This example demonstrates superposition’s power in quantum computing. By handling multiple possibilities simultaneously, quantum computers can solve certain types of problems, like searching, much faster than traditional computers. This principle is what drives the potential for quantum computing to revolutionize fields like cryptography, complex system simulations, and optimization problems in various industries.
Entanglement
Entanglement is a quantum phenomenon where qubits become interconnected and the state of one can instantaneously affect the state of another, regardless of distance. This property is not found in classical bits and is a cornerstone for quantum computing’s potential speed and efficiency.
Let’s explore a real-life example of entanglement in quantum computing through quantum key distribution (QKD), specifically the BB84 protocol, which is used for secure communication.
Example: Secure Communication with Quantum Key Distribution
Imagine two parties, Alice and Bob, wanting to communicate securely. They decide to use QKD to share a secret key, which they’ll use for encrypting and decrypting their messages. The process leverages quantum entanglement.
- Generation of Entangled Qubits: Alice generates a pair of entangled qubits. These qubits are in a special state where the properties of one are intrinsically linked to the properties of the other, regardless of the distance between them.
- Distribution of Qubits: Alice sends one of these entangled qubits to Bob, while keeping the other. Due to entanglement, any change in the state of Alice’s qubit will be mirrored in Bob’s qubit, and vice versa.
- Measuring Qubits: Both Alice and Bob independently measure their qubits using randomly chosen bases. The choice of measurement basis is crucial and is communicated over a classical channel.
- Key Generation: The measurements made by Alice and Bob, thanks to entanglement, will be correlated. They use these correlated results to generate a shared secret key.
- Eavesdropping Detection: If an eavesdropper, say Eve, tries to intercept and measure the qubits, the entanglement is disturbed. This disturbance introduces detectable anomalies in the correlation pattern between Alice’s and Bob’s measurements, alerting them to the presence of an eavesdropper.
Implications
This example illustrates the practical application of quantum entanglement in quantum computing, specifically for secure communication. Entanglement ensures that any attempt at interception can be detected, making QKD a highly secure method of key exchange. Such quantum communication methods have profound implications for cybersecurity, making them a pivotal area in the field of AI and digital transformation. As these technologies evolve, they promise to redefine the standards of data security and privacy.
The Evolution of the Qubit
Early Concepts
The theoretical groundwork for quantum computing, and by extension qubits, was laid in the early 20th century with the development of quantum mechanics. However, it wasn’t until the 1980s that the concept of quantum computing began to take shape, thanks to physicists like Richard Feynman and David Deutsch.
The Birth of Quantum Computing
In 1994, Peter Shor’s algorithm for factoring large numbers exponentially faster than classical computers brought significant attention to quantum computing. This marked a turning point, highlighting the potential of qubits to solve complex problems more efficiently.
How Does a Qubit Work?
Unlike a classical bit, a qubit uses properties like electron spin or photon polarization to represent data. The most common types of qubits include:
- Superconducting Qubits: Utilize the superconductivity properties of materials to create and maintain quantum states.
- Trapped Ion Qubits: Use ions trapped in electromagnetic fields, manipulated with lasers.
- Topological Qubits: Based on exotic materials, promising greater stability and reduced error rates.
Qubits vs Classical Bits
The key difference between qubits and classical bits is their ability to process vast amounts of data due to superposition and entanglement. This enables quantum computers to perform certain calculations much faster than classical computers.
Practical Applications
Quantum computing, fueled by qubits, promises advancements in various fields, including:
- Cryptography: Quantum computers could potentially break many of the cryptographic systems currently in use.
- Drug Discovery: Simulating molecular structures for drug development could become much faster.
- Optimization Problems: Solutions for complex optimization problems in logistics, finance, and AI.
Conclusion
Understanding qubits is crucial for anyone looking to become an experienced practitioner in the quantum computing space. They represent not just a technological leap but a paradigm shift in computing. While quantum computing is still in its nascent stages, its potential is immense, and qubits are at its core. As we advance, the role of qubits in driving digital transformation and AI will become increasingly significant.
With this knowledge, you can confidently discuss the intricacies of qubits and quantum computing, marking yourself as a knowledgeable individual in this cutting-edge field.
