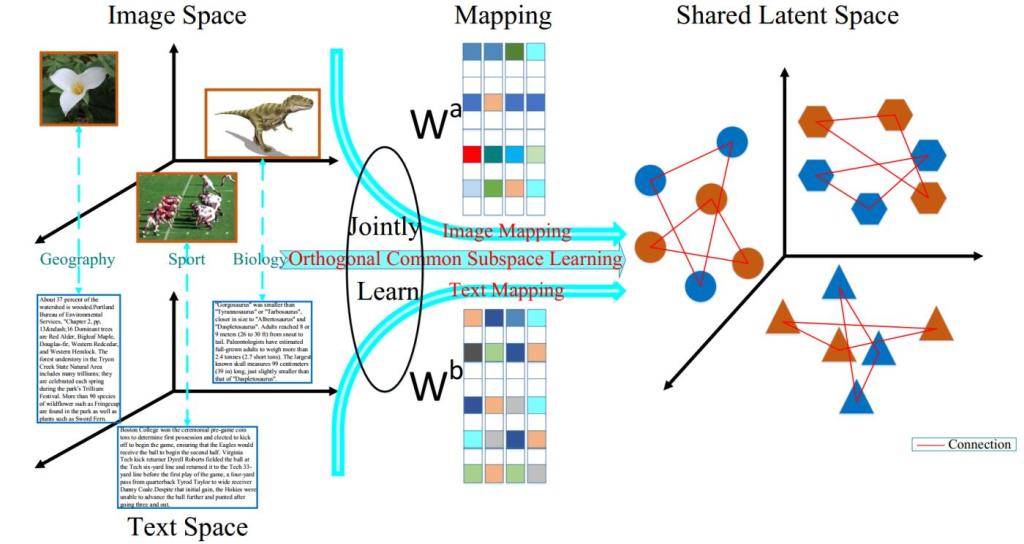
Introduction:
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have brought about a paradigm shift, particularly in the realm of machine learning. As these technologies evolve, there is an increasing emphasis on multi-modal learning. Multi-modal learning revolves around the idea of integrating information from different sources or ‘modalities’ to enhance the learning process. This can include visual data, audio data, text, and even haptic feedback, among others. In this post, we delve deep into the concept of fusion strategies, which is the heart of multi-modal learning, and how AI systems should combine these different modalities for effective learning outcomes.
What is Fusion?
To fully appreciate the power of multi-modal learning, we first need to understand what ‘fusion’ means in this context. Fusion, in the realm of AI and machine learning, refers to the process of integrating various data modalities to produce more nuanced and reliable results than would be possible using a single modality.
Imagine a scenario where an AI system is trained to transcribe a conversation. If the system has only audio data to rely upon, it may struggle with accents, ambient noise, or overlapping speech. However, if the AI can also access video data—lip movements, facial expressions—it can leverage this additional modality to improve transcription accuracy. This is an example of fusion in action.
Types of Fusion Strategies
Fusion strategies can be broadly classified into three categories: Early Fusion, Late Fusion, and Hybrid Fusion.
1. Early Fusion: Early fusion, also known as feature-level fusion, involves combining different modalities at the input level before they are processed by the model. The integrated data is then fed into the model for processing. This approach can capture the correlations between different modalities at the cost of being computationally expensive and requiring all modalities to be available at the time of input.
2. Late Fusion: Late fusion, also known as decision-level fusion, involves processing each modality separately through different models and combining the outputs at the end. This allows the model to make decisions based on the individual strengths of each modality. It is less computationally intensive than early fusion and can handle modalities being available at different times. However, it may not capture the correlations between modalities as effectively as early fusion.
3. Hybrid Fusion: As the name suggests, hybrid fusion is a blend of early and late fusion strategies. It aims to leverage the strengths of both approaches, capturing correlations between modalities while also being flexible and less demanding computationally. Hybrid fusion strategies usually involve performing early fusion on some modalities and late fusion on others, or applying early fusion and then adding additional modalities via late fusion.
How Should an AI System Combine Information from Different Modalities?
Choosing the right fusion strategy depends on the nature of the task, the modalities involved, and the specific requirements of the system.
1. Consider the Nature of the Task: Tasks that require an understanding of the correlation between modalities may benefit from early fusion. For example, in video captioning, the visual and audio components are closely related, and combining these modalities early in the process can enhance the model’s performance.
2. Evaluate the Modalities: The characteristics of the modalities also influence the choice of fusion strategy. For instance, when dealing with high-dimensional data like images and video, early fusion might be computationally prohibitive. In such cases, late fusion might be a more feasible approach.
3. Assess System Requirements: If real-time processing and flexibility with asynchronous modalities are crucial, late fusion or hybrid fusion might be the preferred choice.
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to fusion strategies in multi-modal learning. The key lies in understanding the technicalities of the task at hand, the modalities in play, and the specific requirements of the system, and then selecting the fusion strategy that best aligns with these factors.
Recent Advances in Fusion Strategies
Despite the challenges, researchers are pushing the boundaries and continually developing innovative fusion strategies for multi-modal learning. Several promising directions in this field include:
1. Cross-modal Attention Mechanisms: Attention mechanisms have been a popular technique in machine learning, initially proving their worth in Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. They have now made their way into the realm of multi-modal learning, with cross-modal attention mechanisms proving particularly promising. These models can learn to “pay attention” to relevant features across different modalities, leading to more effective fusion and ultimately better performance.
2. Graph-based Fusion: Graph-based methods are another area of interest. Here, different modalities are represented as nodes in a graph, with the edges denoting interactions between these modalities. The graph structure allows for a rich representation of the relationships between modalities, and it can be a powerful tool for fusion.
3. Deep Fusion Techniques: With the advent of deep learning, more complex fusion techniques have become feasible. For instance, multi-layer fusion strategies can execute fusion at different levels of abstraction, enabling the model to capture both low-level and high-level interactions between modalities.
The Role of Context in Fusion Strategies
The decision of which fusion strategy to adopt is not solely determined by the nature of the task or the characteristics of the modalities. The context in which the AI system operates also plays a significant role. For instance, if an AI system is designed to operate in an environment where network latency is high or where computing resources are limited, a late fusion strategy could be more appropriate due to its lower computational requirements.
Similarly, if the system is deployed in a setting where certain modalities might be unavailable or unreliable—such as in a noisy environment where audio data might be compromised—a late or hybrid fusion strategy could be more suitable as they offer greater flexibility in dealing with missing or uncertain data.
The Importance of Evaluation Metrics
The choice of fusion strategy should also be informed by the evaluation metrics that are important for the task at hand. Different fusion strategies might optimize for different aspects of performance. For example, an early fusion strategy might lead to higher accuracy by capturing intricate correlations between modalities, while a late fusion strategy might offer faster processing times or better handling of missing or asynchronous data.
Hence, it’s important to clearly define the success metrics for your AI system—be it accuracy, speed, robustness, or some other criterion—and to choose a fusion strategy that aligns with these objectives.
The Future of Fusion Strategies
Given the rapid progress in AI and machine learning, it’s clear that the future holds exciting possibilities for fusion strategies in multi-modal learning.
With advancements in technologies like 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT), we can expect an explosion in the availability of diverse and rich data from multiple modalities. This will provide unprecedented opportunities for multi-modal learning, and the demand for effective and efficient fusion strategies will only grow.
In the future, we can anticipate more sophisticated fusion strategies that leverage the power of deep learning and other advanced techniques to capture complex correlations between modalities and deliver superior performance. For instance, we could see fusion strategies that dynamically adapt to the context, selecting different approaches for different tasks or environments. Or we could see strategies that incorporate elements of reinforcement learning, allowing the AI system to learn and improve its fusion strategy over time based on feedback.
At the same time, we must also be mindful of the challenges that lie ahead. As we deal with more and complex data from diverse modalities, issues like data privacy, algorithmic fairness, and interpretability will become increasingly important. As such, the development of fusion strategies will need to be guided not only by considerations of performance and efficiency but also by ethical and societal considerations.
Conclusion
Fusion strategies are at the heart of multi-modal learning, and they hold the key to unlocking the full potential of AI systems. By carefully considering the task, the modalities, the context, and the desired outcomes, we can select the most effective fusion strategy and build AI systems that are truly greater than the sum of their parts. As we look to the future, the possibilities for fusion strategies in multi-modal learning are exciting and virtually limitless. The journey has only just begun, and the destination promises to be nothing short of revolutionary.