Introduction: Why Determinism Matters to Customer Experience
Customer Experience (CX) leaders increasingly rely on AI to shape how customers are served, advised, and supported. From virtual agents and recommendation engines to decision-support tools for frontline employees, AI is now embedded directly into the moments that define customer trust.
In this context, deterministic inference is not a technical curiosity, it is a CX enabler. It determines whether customers receive consistent answers, whether agents trust AI guidance, and whether organizations can scale personalized experiences without introducing confusion, risk, or inequity.
This article reframes deterministic inference through a CX lens. It begins with an intuitive explanation, then explores how determinism influences customer trust, operational consistency, and experience quality in AI-driven environments. By the end, you should be able to articulate why deterministic inference is central to modern CX strategy and how it shapes the future of AI-powered customer engagement.
Part 1: Deterministic Thinking in Everyday Customer Experiences
At a basic level, customers expect consistency.
If a customer:
- Checks an order status online
- Calls the contact center later
- Chats with a virtual agent the next day
They expect the same answer each time.
This expectation maps directly to determinism.
A Simple CX Analogy
Consider a loyalty program:
- Input: Customer ID + purchase history
- Output: Loyalty tier and benefits
If the system classifies a customer as Gold on Monday and Silver on Tuesday—without any change in behavior—the experience immediately degrades. Trust erodes.
Customers may not know the word “deterministic,” but they feel its absence instantly.
Part 2: What Inference Means in CX-Oriented AI Systems
In CX, inference is the moment AI translates customer data into action.
Examples include:
- Deciding which response a chatbot gives
- Recommending next-best actions to an agent
- Determining eligibility for refunds or credits
- Personalizing offers or messaging
Inference is where customer data becomes customer experience.
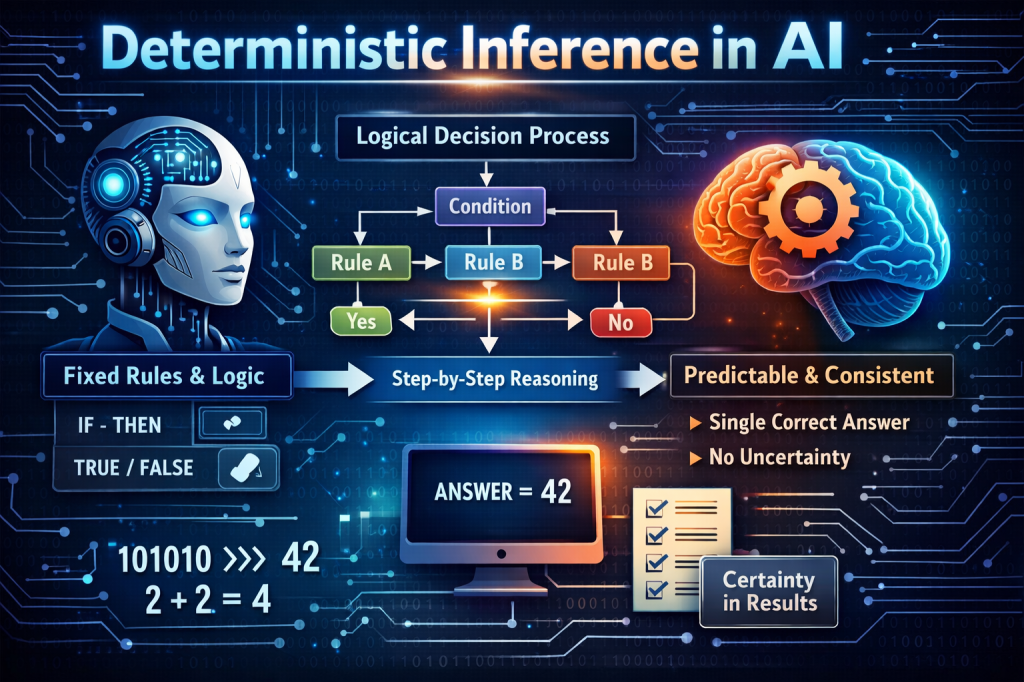
Part 3: Deterministic Inference Defined for CX
From a CX perspective, deterministic inference means:
Given the same customer context, business rules, and AI model state, the system produces the same customer-facing outcome every time.
This does not mean experiences are static. It means they are predictably adaptive.
Why This Is Non-Trivial in Modern CX AI
Many CX AI systems introduce variability by design:
- Generative chat responses – Replies produced by an artificial intelligence (AI) system that uses machine learning to create original, human-like text in real-time, rather than relying on predefined scripts or rules. These responses are generated based on patterns the AI has learned from being trained on vast amounts of existing data, such as books, web pages, and conversation examples.
- Probabilistic intent classification – a machine learning method used in natural language processing (NLP) to identify the purpose behind a user’s input (such as a chat message or voice command) by assigning a probability distribution across a predefined set of potential goals, rather than simply selecting a single, most likely intent.
- Dynamic personalization models – Refer to systems that automatically tailor digital content and user experiences in real time based on an individual’s unique preferences, past behaviors, and current context. This approach contrasts with static personalization, which relies on predefined rules and broad customer segments.
- Agentic workflows – An AI-driven process where autonomous “agents” independently perform multi-step tasks, make decisions, and adapt to changing conditions to achieve a goal, requiring minimal human oversight. Unlike traditional automation that follows strict rules, agentic workflows use AI’s reasoning, planning, and tool-use abilities to handle complex, dynamic situations, making them more flexible and efficient for tasks like data analysis, customer support, or IT management.
Without guardrails, two customers with identical profiles may receive different experiences—or the same customer may receive different answers across channels.
Part 4: Deterministic vs. Probabilistic CX Experiences
Probabilistic CX (Common in Generative AI)
Probabilistic inference can produce varied but plausible responses.
Example:
Customer asks: “What fees apply to my account?”
Possible outcomes:
- Response A mentions two fees
- Response B mentions three fees
- Response C phrases exclusions differently
All may be linguistically correct, but CX consistency suffers.
Deterministic CX
With deterministic inference:
- Fee logic is fixed
- Eligibility rules are stable
- Response content is governed
The customer receives the same answer regardless of channel, agent, or time.
Part 5: Why Deterministic Inference Is Now a CX Imperative
1. Omnichannel Consistency
A customer-centric strategy that creates a seamless, integrated, and consistent brand experience across all customer touchpoints, whether online (website, app, social media, email) or offline (physical store), allowing customers to move between channels effortlessly with a unified journey. It breaks down silos between channels, using customer data to deliver personalized, real-time interactions that build loyalty and drive conversions, unlike multichannel, which often keeps channels separate.
Customers move fluidly across a marketing centered ecosystem: (Consisting typically of)
- Web
- Mobile
- Chat
- Voice
- Human agents
Deterministic inference ensures that AI behaves like a single brain, not a collection of loosely coordinated tools.
2. Trust and Perceived Fairness
Trust and perceived fairness are two of the most fragile and valuable assets in customer experience. AI systems, particularly those embedded in service, billing, eligibility, and recovery workflows, directly influence whether customers believe a company is acting competently, honestly, and equitably.
Deterministic inference plays a central role in reinforcing both.
Defining Trust and Fairness in a CX Context
Customer Trust can be defined as:
The customer’s belief that an organization will behave consistently, competently, and in the customer’s best interest across interactions.
Trust is cumulative. It is built through repeated confirmation that the organization “remembers,” “understands,” and “treats me the same way every time under the same conditions.”
Perceived Fairness refers to:
The customer’s belief that decisions are applied consistently, without arbitrariness, favoritism, or hidden bias.
Importantly, perceived fairness does not require that outcomes always favor the customer—only that outcomes are predictable, explainable, and consistently applied.
How Non-Determinism Erodes Trust
When AI-driven CX systems are non-deterministic, customers may experience:
- Different answers to the same question on different days
- Different outcomes depending on channel (chat vs. voice vs. agent)
- Inconsistent eligibility decisions without explanation
From the customer’s perspective, this variability feels indistinguishable from:
- Incompetence
- Lack of coordination
- Unfair treatment
Even if every response is technically “reasonable,” inconsistency signals unreliability.
How Deterministic Inference Reinforces Trust
Deterministic inference ensures that:
- Identical customer contexts yield identical decisions
- Policy interpretation does not drift between interactions
- AI behavior is stable over time unless explicitly changed
This creates what customers experience as institutional memory and coherence.
Customers begin to trust that:
- The system knows who they are
- The rules are real (not improvised)
- Outcomes are not arbitrary
Trust, in this sense, is not emotional—it is structural.
Determinism as the Foundation of Perceived Fairness
Fairness in CX is primarily about consistency of application.
Deterministic inference supports fairness by:
- Applying the same logic to all customers with equivalent profiles
- Eliminating accidental variance introduced by sampling or generative phrasing
- Enabling clear articulation of “why” a decision occurred
When determinism is present, organizations can say:
“Anyone in your situation would have received the same outcome.”
That statement is nearly impossible to defend in a non-deterministic system.
Real-World CX Examples
Example 1: Billing Disputes
A customer disputes a late fee.
- Non-deterministic system:
- Chatbot waives the fee
- Phone agent denies the waiver
- Follow-up email escalates to a partial credit
The customer concludes the process is arbitrary and learns to “channel shop.”
- Deterministic system:
- Eligibility rules are fixed
- All channels return the same decision
- Explanation is consistent
Even if the fee is not waived, the experience feels fair.
Example 2: Service Recovery Offers
Two customers experience the same outage.
- Non-deterministic AI generates different goodwill offers
- One customer receives a credit, the other an apology only
Perceived inequity emerges immediately—often amplified on social media.
Deterministic inference ensures:
- Outage classification is stable
- Compensation logic is uniformly applied
Example 3: Financial or Insurance Eligibility
In lending, insurance, or claims environments:
- Customers frequently recheck decisions
- Outcomes are scrutinized closely
Deterministic inference enables:
- Reproducible decisions during audits
- Clear explanations to customers
- Reduced escalation to human review
The result is not just compliance—it is credibility.
Trust, Fairness, and Escalation Dynamics
Inconsistent AI decisions increase:
- Repeat contacts
- Supervisor escalations
- Customer complaints
Deterministic systems reduce these behaviors by removing perceived randomness.
When customers believe outcomes are consistent and rule-based, they are less likely to challenge them—even unfavorable ones.
Key CX Takeaway
Deterministic inference does not guarantee positive outcomes for every customer.
What it guarantees is something more important:
- Consistency over time
- Uniform application of rules
- Explainability of decisions
These are the structural prerequisites for trust and perceived fairness in AI-driven customer experience.
3. Agent Confidence and Adoption
Frontline employees quickly disengage from AI systems that contradict themselves.
Deterministic inference:
- Reinforces agent trust
- Reduces second-guessing
- Improves adherence to AI recommendations
Part 6: CX-Focused Examples of Deterministic Inference
Example 1: Contact Center Guidance
- Input: Customer tenure, sentiment, issue type
- Output: Recommended resolution path
If two agents receive different guidance for the same scenario, experience variance increases.
Example 2: Virtual Assistants
A customer asks the same question on chat and voice.
Deterministic inference ensures:
- Identical policy interpretation
- Consistent escalation thresholds
Example 3: Personalization Engines
Determinism ensures that personalization feels intentional – not random.
Customers should recognize patterns, not unpredictability.
Part 7: Deterministic Inference and Generative AI in CX
Generative AI has fundamentally changed how organizations design and deliver customer experiences. It enables natural language, empathy, summarization, and personalization at scale. At the same time, it introduces variability that if left unmanaged can undermine consistency, trust, and operational control.
Deterministic inference is the mechanism that allows organizations to harness the strengths of generative AI without sacrificing CX reliability.
Defining the Roles: Determinism vs. Generation in CX
To understand how these work together, it is helpful to separate decision-making from expression.
Deterministic Inference (CX Context)
The process by which customer data, policy rules, and business logic are evaluated in a repeatable way to produce a fixed outcome or decision.
Examples include:
- Eligibility decisions
- Next-best-action selection
- Escalation thresholds
- Compensation logic
Generative AI (CX Context)
The process of transforming decisions or information into human-like language, tone, or format.
Examples include:
- Writing a response to a customer
- Summarizing a case for an agent
- Rephrasing policy explanations empathetically
In mature CX architectures, generative AI should not decide what happens -only how it is communicated.
Why Unconstrained Generative AI Creates CX Risk
When generative models are allowed to perform inference implicitly, several CX risks emerge:
- Policy drift: responses subtly change over time
- Inconsistent commitments: different wording implies different entitlements
- Hallucinated exceptions or promises
- Channel-specific discrepancies
From the customer’s perspective, these failures manifest as:
- “The chatbot told me something different.”
- “Another agent said I was eligible.”
- “Your email says one thing, but your app says another.”
None of these are technical errors—they are experience failures caused by nondeterminism.
How Deterministic Inference Stabilizes Generative CX
Deterministic inference creates a stable backbone that generative AI can safely operate on.
It ensures that:
- Business decisions are made once, not reinterpreted
- All channels reference the same outcome
- Changes occur only when rules or models are intentionally updated
Generative AI then becomes a presentation layer, not a decision-maker.
This separation mirrors proven software principles: logic first, interface second.
Canonical CX Architecture Pattern
A common and effective pattern in production CX systems is:
- Deterministic Decision Layer
- Evaluates customer context
- Applies rules, models, and thresholds
- Produces explicit outputs (e.g., “eligible = true”)
- Generative Language Layer
- Translates decisions into natural language
- Adjusts tone, empathy, and verbosity
- Adapts phrasing by channel
This pattern allows organizations to scale generative CX safely.
Real-World CX Examples
Example 1: Policy Explanations in Contact Centers
- Deterministic inference determines:
- Whether a fee can be waived
- The maximum allowable credit
- Generative AI determines:
- How the explanation is phrased
- The level of empathy
- Channel-appropriate tone
The outcome remains fixed; the expression varies.
Example 2: Virtual Agent Responses
A customer asks: “Can I cancel without penalty?”
- Deterministic layer evaluates:
- Contract terms
- Timing
- Customer tenure
- Generative layer constructs:
- A clear, empathetic explanation
- Optional next steps
This prevents the model from improvising policy interpretation.
Example 3: Agent Assist and Case Summaries
In agent-assist tools:
- Deterministic inference selects next-best-action
- Generative AI summarizes context and rationale
Agents see consistent guidance while benefiting from flexible language.
Example 4: Service Recovery Messaging
After an outage:
- Deterministic logic assigns compensation tiers
- Generative AI personalizes apology messages
Customers receive equitable treatment with human-sounding communication.
Determinism, Generative AI, and Compliance
In regulated industries, this separation is critical.
Deterministic inference enables:
- Auditability of decisions
- Reproducibility during disputes
- Clear separation of logic and language
Generative AI, when constrained, does not threaten compliance—it enhances clarity.
Part 8: Determinism in Agentic CX Systems
As customer experience platforms evolve, AI systems are no longer limited to answering questions or generating text. Increasingly, they are becoming agentic – capable of planning, deciding, acting, and iterating across multiple steps to resolve customer needs.
Agentic CX systems represent a step change in automation power. They also introduce a step change in risk.
Deterministic inference is what allows agentic CX systems to operate safely, predictably, and at scale.
Defining Agentic AI in a CX Context
Agentic AI (CX Context) refers to AI systems that can:
- Decompose a customer goal into steps
- Decide which actions to take
- Invoke tools or workflows
- Observe outcomes and adjust behavior
Examples include:
- An AI agent that resolves a billing issue end-to-end
- A virtual assistant that coordinates between systems (CRM, billing, logistics)
- An autonomous service agent that proactively reaches out to customers
In CX, agentic systems are effectively digital employees operating customer journeys.
Why Agentic CX Amplifies the Need for Determinism
Unlike single-response AI, agentic systems:
- Make multiple decisions per interaction
- Influence downstream systems
- Accumulate effects over time
Without determinism, small variations compound into large experience divergence.
This leads to:
- Different resolution paths for identical customers
- Inconsistent journey lengths
- Unpredictable escalation behavior
- Inability to reproduce or debug failures
In CX terms, the journey itself becomes unstable.
Deterministic Inference as Journey Control
Deterministic inference acts as a control system for agentic CX.
It ensures that:
- Identical customer states produce identical action plans
- Tool selection follows stable rules
- State transitions are predictable
Rather than improvising journeys, agentic systems execute governed playbooks.
This transforms agentic AI from a creative actor into a reliable operator.
Determinism vs. Emergent Behavior in CX
Emergent behavior is often celebrated in AI research. In CX, it is usually a liability.
Customers do not want:
- Creative interpretations of policy
- Novel escalation strategies
- Personalized but inconsistent journeys
Determinism constrains emergence to expression, not action.
Canonical Agentic CX Architecture
Mature agentic CX systems typically separate concerns:
- Deterministic Orchestration Layer
- Defines allowable actions
- Enforces sequencing rules
- Governs state transitions
- Probabilistic Reasoning Layer
- Interprets intent
- Handles ambiguity
- Generative Interaction Layer
- Communicates with customers
- Explains actions
Determinism anchors the system; intelligence operates within bounds.
Real-World CX Examples
Example 1: End-to-End Billing Resolution Agent
An agentic system resolves billing disputes autonomously.
- Deterministic logic controls:
- Eligibility checks
- Maximum credits
- Required verification steps
- Agentic behavior sequences actions:
- Retrieve invoice
- Apply adjustment
- Notify customer
Two identical disputes follow the same path, regardless of timing or channel.
Example 2: Proactive Service Outreach
An AI agent monitors service degradation and proactively contacts customers.
Deterministic inference ensures:
- Outreach thresholds are consistent
- Priority ordering is fair
- Messaging triggers are stable
Without determinism, customers perceive favoritism or randomness.
Example 3: Escalation Management
An agentic CX system decides when to escalate to a human.
Deterministic rules govern:
- Sentiment thresholds
- Time-in-journey limits
- Regulatory triggers
This prevents over-escalation, under-escalation, and agent mistrust.
Debugging, Auditability, and Learning
Agentic systems without determinism are nearly impossible to debug.
Deterministic inference enables:
- Replay of customer journeys
- Root-cause analysis
- Safe iteration on rules and models
This is essential for continuous CX improvement.
Part 9: Strategic CX Implications
Deterministic inference is not merely a technical implementation detail – it is a strategic enabler that determines whether AI strengthens or destabilizes a customer experience operating model.
At scale, CX strategy is less about individual interactions and more about repeatable experience outcomes. Determinism is what allows AI-driven CX to move from experimentation to institutional capability.
Defining Strategic CX Implications
From a CX leadership perspective, a strategic implication is not about what the AI can do, but:
- How reliably it can do it
- How safely it can scale
- How well it aligns with brand, policy, and regulation
Deterministic inference directly influences these dimensions.
1. Scalable Personalization Without Fragmentation
Scalable personalization means:
Delivering tailored experiences to millions of customers without introducing inconsistency, inequity, or operational chaos.
Without determinism:
- Personalization feels random
- Customers struggle to understand why they received a specific treatment
- Frontline teams cannot explain or defend outcomes
With deterministic inference:
- Personalization logic is explicit and repeatable
- Customers with similar profiles experience similar journeys
- Variations are intentional, not accidental
Real-world example:
A telecom provider personalizes retention offers.
- Deterministic logic assigns offer tiers based on tenure, usage, and churn risk
- Generative AI personalizes messaging tone and framing
Customers perceive personalization as thoughtful—not arbitrary.
2. Governable Automation and Risk Management
Governable automation refers to:
The ability to control, audit, and modify automated CX behavior without halting operations.
Deterministic inference enables:
- Clear ownership of decision logic
- Predictable effects of policy changes
- Safe rollout and rollback of AI capabilities
Without determinism, automation becomes opaque and risky.
Real-world example:
An insurance provider automates claims triage.
- Deterministic inference governs eligibility and routing
- Changes to rules can be simulated before deployment
This reduces regulatory exposure while improving cycle time.
3. Experience Quality Assurance at Scale
Traditional CX quality assurance relies on sampling human interactions.
AI-driven CX requires:
System-level assurance that experiences conform to defined standards.
Deterministic inference allows organizations to:
- Test AI behavior before release
- Detect drift when logic changes
- Guarantee experience consistency across channels
Real-world example:
A bank tests AI responses to fee disputes across all channels.
- Deterministic logic ensures identical outcomes in chat, voice, and branch support
- QA focuses on tone and clarity, not decision variance
4. Regulatory Defensibility and Audit Readiness
In regulated industries, CX decisions are often legally material.
Deterministic inference enables:
- Reproduction of past decisions
- Clear explanation of why an outcome occurred
- Evidence that policies are applied uniformly
Real-world example:
A lender responds to a customer complaint about loan denial.
- Deterministic inference allows the exact decision path to be replayed
- The institution demonstrates fairness and compliance
This shifts AI from liability to asset.
5. Organizational Alignment and Operating Model Stability
CX failures are often organizational, not technical.
Deterministic inference supports:
- Alignment between policy, legal, CX, and operations
- Clear translation of business intent into system behavior
- Reduced reliance on tribal knowledge
Real-world example:
A global retailer standardizes return policies across regions.
- Deterministic logic encodes policy variations explicitly
- Generative AI localizes communication
The experience remains consistent even as organizations scale.
6. Economic Predictability and ROI Measurement
From a strategic standpoint, leaders must justify AI investments.
Deterministic inference enables:
- Predictable cost-to-serve
- Stable deflection and containment metrics
- Reliable attribution of outcomes to decisions
Without determinism, ROI analysis becomes speculative.
Real-world example:
A contact center deploys AI-assisted resolution.
- Deterministic guidance ensures consistent handling time reductions
- Leadership can confidently scale investment
Part 10: The Future of Deterministic Inference in CX
Key trends include:
- Experience Governance by Design – A proactive approach that embeds compliance, ethics, risk management, and operational rules directly into the creation of systems, products, or services from the very start, making them inherently aligned with desired outcomes, rather than adding them as an afterthought. It shifts governance from being a restrictive layer to a foundational enabler, ensuring that systems are built to be effective, trustworthy, and sustainable, guiding user behavior and decision-making intuitively.
- Hybrid Experience Architectures – A strategic framework that combines and integrates different computing, physical, or organizational elements to create a unified, flexible, and optimized user experience. The specific definition varies by context, but it fundamentally involves leveraging the strengths of disparate systems through seamless integration and orchestration.
- Audit-Ready Customer Journeys
Every AI-driven interaction reproducible and explainable. - Trust as a Differentiator – A brand’s proven reliability, integrity, and commitment to its promises become the primary reason customers choose it over competitors, especially when products are similar, leading to higher prices, reduced friction, and increased loyalty by building confidence and reducing perceived risk. It’s the belief that a company will act in the customer’s best interest, providing a competitive advantage difficult to replicate.
Conclusion: Determinism as the Backbone of Trusted CX
Deterministic inference is foundational to trustworthy, scalable, AI-driven customer experience. It ensures that intelligence does not come at the cost of consistency—and that automation enhances, rather than undermines, customer trust.
As AI becomes inseparable from CX, determinism will increasingly define which organizations deliver coherent, defensible, and differentiated experiences and which struggle with fragmentation and erosion of trust.
Please join us on (Spotify) as we discuss this and other AI / CX topics.