Introduction:
In yesterday’s post we discussed how emotion recognition AI can be leveraged in your customer experience management strategy. Today we decided to dive a bit deeper into this particular sector of AI and see if we can add clarity to the topic, as it can be controversial.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has many applications and it has pervaded all areas of human endeavor, and the realm of marketing has not been exempt from this wave. Among its numerous applications, emotion recognition AI is emerging as a game-changing technology for marketers. This blog post delves into how emotion recognition AI works, its implications in digital marketing, and how small to medium businesses can harness this technology today. We will also discuss the implications of the intertwining of facial recognition, emotion recognition, and data privacy, drawing from real-world examples like Clearview AI.
Emotion Recognition AI: An Overview
Emotion recognition AI is a form of technology that allows machines to identify and interpret human emotions. It leverages machine learning and deep learning to analyze various forms of data, including facial expressions, speech patterns, body language, text sentiment, and physiological signals.
The process begins with data collection. Facial expression analysis, for instance, involves gathering visual data through cameras or other imaging devices. Speech emotion recognition requires audio data, usually collected via microphones.
Once the data is collected, it is processed using various algorithms. In facial expression analysis, facial landmarks (like corners of the mouth or the eyebrows) are identified, and changes in these landmarks are used to interpret emotions. In speech analysis, features such as pitch, intensity, and tempo are extracted and analyzed.
These processed data features are then fed into a machine learning model. This model has been trained on a vast amount of labeled data, learning to associate specific features with corresponding emotions. When presented with new data, it can make educated predictions about the person’s emotional state. But as we mentioned earlier, we need to dive into these techniques a bit further and hopefully this will add clarity on the data required and training techniques of the models.
The Intricacies of Data Collection and Model Training in Emotion Recognition AI
The data collection process in emotion recognition AI is an integral part that determines the accuracy and effectiveness of emotion predictions. The data collection can occur through multiple mediums depending on the type of emotion recognition being deployed – visual for facial expressions, audio for voice modulations, text for sentiment analysis, and biometrics for physiological responses.
Facial Expression Analysis
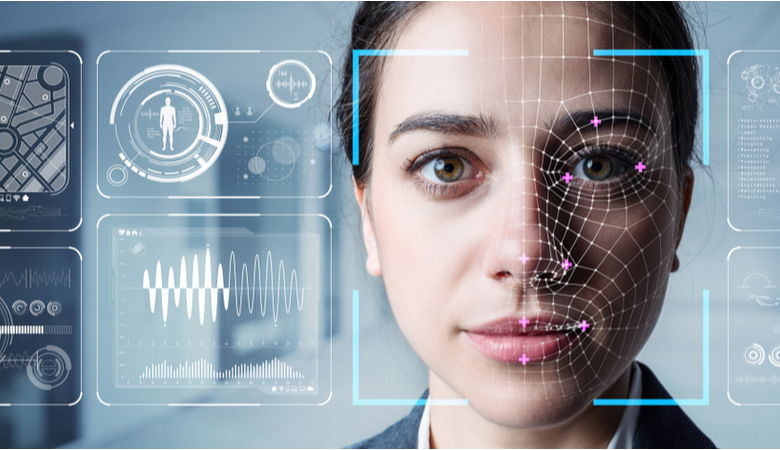
In facial expression analysis, a common method of emotion recognition, data is collected through cameras or imaging devices. For instance, if a business wants to gauge customer reactions to a new product in a store, they could set up cameras to capture customer facial expressions. Companies can also use webcams or smartphone cameras to collect this data in digital interactions, provided they have received user consent.
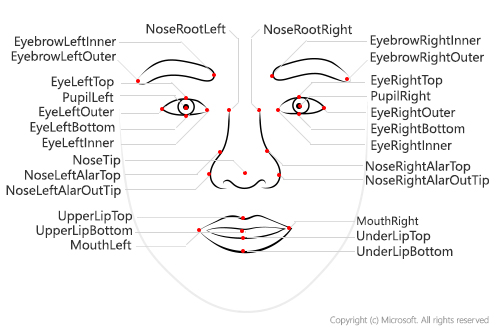
The data is primarily composed of facial landmarks – specific points on the face that correspond to different features, such as the mouth, eyebrows, and eyes. The movement and position of these points, for example, the furrowing of brows or the curving of lips, are used to determine the emotional state.
Speech Emotion Recognition
In speech emotion recognition, audio data is collected through microphones or during phone calls. For instance, a call center could use emotion recognition AI to monitor customer service interactions.
In this scenario, features such as pitch (highness or lowness of the voice), intensity (loudness), tempo (speed of speech), and even the pauses between words are extracted from the audio data. These features provide indicators of the speaker’s emotional state.
Textual Sentiment Analysis
For textual sentiment analysis, data can be collected from various sources such as social media posts, customer reviews, or email interactions. For example, a restaurant might want to gauge customer sentiment about a new menu item by analyzing online reviews. The words, phrases, and overall tone used in these reviews serve as data points for determining sentiment.
Physiological Signals
In some advanced use-cases, physiological signals such as heart rate, skin temperature, or galvanic skin response can be used to infer emotional states. Devices like smartwatches, fitness bands, or specialized wearable devices collect this data.
For instance, a health app might analyze changes in heart rate data during a workout to understand if users find the exercise routine exciting or stressful.
Model Training and Emotion Recognition
Once the data is collected and the relevant features extracted, it’s then labeled to correspond to various emotions. For facial expression analysis, the labels might include “happy,” “sad,” “angry,” “surprised,” and so on. For sentiment analysis, labels might be “positive,” “negative,” or “neutral.”
This labeled data is then used to train machine learning models. At a high level, training involves inputting the feature data into the model and allowing the model to make a prediction about the emotion. The model’s prediction is then compared with the actual label, and the model adjusts its internal parameters to reduce the difference between the prediction and the actual label.
Consider the example of the restaurant collecting data from customer reviews. If the model encounters a review saying, “The new dish was fantastic and made my day,” it might initially predict a neutral sentiment. However, the actual label for this review would be “positive.” The model would then adjust its parameters to increase the likelihood of predicting “positive” for similar reviews in the future.
This process is repeated for thousands, if not millions, of data points. Over time, the model learns to associate certain features with specific emotions accurately. The trained model can then be used to predict the emotional state of new, unlabeled data.
Different machine learning algorithms and architectures can be used for model training, including decision trees, support vector machines, and neural networks. Deep learning models, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image data and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) or transformers for text and audio data, have proven particularly effective due to their ability to learn complex patterns and dependencies in the data.
In conclusion, the collection of high-quality, representative data and the proper training of machine learning models are crucial steps in developing effective emotion recognition AI systems. These systems, while powerful, should always be employed with due consideration for user consent, data privacy, and ethical implications.
Emotion Recognition AI in Digital Marketing
The crux of successful marketing has always been understanding consumers. Emotion recognition AI can take this understanding to unprecedented depths, providing insights into how customers feel, not just what they say or do.
Personalization: Emotion recognition AI can help businesses personalize their marketing strategies. For instance, by understanding a user’s emotional state when they interact with a product or service, businesses can tailor their offerings or communication to match the user’s mood, thereby enhancing user experience and engagement.
Sentiment Analysis: Businesses can use emotion recognition AI to perform real-time sentiment analysis on social media or other platforms. This can provide valuable feedback on their products or services, enabling them to make necessary adjustments swiftly.
Ad Testing: Businesses can also use this technology to test their advertisements. By observing the emotional responses elicited by an ad, they can refine the content to evoke the desired emotions, increasing the ad’s effectiveness.
Leveraging Emotion Recognition AI for SMBs
Small to medium-size businesses (SMBs) can use emotion recognition AI to gain a competitive edge in several ways.
Customer Service: SMBs can use emotion recognition AI in their customer service to identify dissatisfied customers or escalate high-stress situations, thereby enhancing customer experience and loyalty.
Product Development: By analyzing customer reactions to various product features, SMBs can prioritize enhancements that resonate emotionally with their target audience, thereby improving their product-market fit.
Content Marketing: SMBs can use sentiment analysis to identify emotional trends in user-generated content or social media chatter about their brand, allowing them to respond appropriately and enhance their brand image.
Several tools and services can help SMBs harness emotion recognition AI. These range from emotion AI software like Affectiva and Realeyes, which offer emotion analytics for videos, to cloud-based AI services like Microsoft’s Azure Cognitive Services and Google’s Cloud AI, which provide a range of emotion AI capabilities.
Emotion Recognition AI and Data Privacy: A Delicate Balance
While emotion recognition AI has immense potential, its intertwining with facial recognition and data privacy raises several concerns.
Clearview AI provides a relevant example. This company uses facial recognition to scrape billions of images from social media and other online sources, enabling its users to match faces to these scraped images. While Clearview AI has been a powerful tool for law enforcement agencies, it has faced backlash for infringing on privacy rights.
Similarly, emotion recognition AI, which often involves analyzing sensitive data like facial expressions or voice tones, can raise significant privacy concerns. Without clear and stringent regulations, this technology risks being used unethically, potentially leading to unwarranted psychological manipulation or privacy infringement.
Therefore, businesses leveraging emotion recognition AI must adhere to strict ethical guidelines and regulations. They should ensure they obtain informed consent from individuals before collecting their data. They should also commit to transparency about how they use and secure this data.
The Pros and Cons of Emotion Recognition AI in Digital Marketing
Like any technology, emotion recognition AI has its pros and cons in digital marketing.
Pros
- Enhanced Consumer Insights: This technology provides deeper, more nuanced insights into consumers’ emotional states, enabling businesses to tailor their strategies more effectively.
- Improved User Experience: By personalizing user experiences based on their emotional states, businesses can increase customer engagement and loyalty.
- Real-time Feedback: Emotion recognition AI enables businesses to obtain real-time feedback on their products, services, or ads, allowing them to adjust their strategies swiftly.
Cons
- Privacy Concerns: Emotion recognition AI can raise significant privacy concerns, particularly if businesses collect and use emotional data without obtaining informed consent.
- Ethical Implications: There are concerns about potential misuse of the technology, such as psychological manipulation or discrimination based on emotional states.
- Accuracy: While emotion recognition technology has improved dramatically, it is not 100% accurate. Misinterpretations can lead to incorrect inferences or actions, which can harm the business-customer relationship.
Conclusion:
Emotion recognition AI is a powerful tool for digital marketers, offering unprecedented insights into consumer behavior. However, businesses must tread carefully, balancing the benefits of this technology with the need for privacy and ethical considerations. As the technology matures and as we learn to navigate these complexities, the possibilities for emotion recognition AI in digital marketing are indeed limitless.